Los Angeles Air Quality: It’s a topic that hits close to home for Angelenos, a constant hum in the background of daily life. From the hazy smoggy days to the surprisingly clear skies, LA’s air quality is a dynamic, ever-changing story shaped by industry, traffic, wildfires, and even the city’s unique geography. This exploration dives deep into the sources of pollution, its health impacts, monitoring efforts, and the ongoing fight for cleaner air in the City of Angels.
We’ll unpack the science, the politics, and the everyday realities of breathing in LA.
This report will cover the major sources of air pollution in Los Angeles, including industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, wildfires, and construction. We’ll analyze the effects on public health, focusing on vulnerable populations, and explore the monitoring methods and data used to track air quality. Furthermore, we’ll examine existing regulations and policies, innovative technologies, and community engagement efforts aimed at improving air quality in the city.
Sources of Air Pollution in Los Angeles
Los Angeles’ infamous smog is a complex issue stemming from a variety of sources. Understanding these sources is crucial to developing effective mitigation strategies. The major contributors to poor air quality include industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, wildfires, and construction activities, each with unique characteristics and seasonal variations.
Major Sources of Air Pollution in Los Angeles
| Source | Pollutant Type | Contribution Percentage (Estimate) | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Exhaust | Nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), carbon monoxide (CO), ozone (O3) | 40% | Promoting electric vehicles, improving public transportation, stricter vehicle emission standards. |
| Industrial Emissions | Sulfur dioxide (SO2), NOx, PM2.5, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) | 25% | Implementing stricter emission controls on industrial facilities, promoting cleaner technologies. |
| Wildfires | PM2.5, VOCs, carbon dioxide (CO2) | 15% (highly variable depending on wildfire activity) | Improved forest management, controlled burns, public awareness campaigns about wildfire prevention. |
| Construction Activities | PM10, dust | 10% | Implementing dust control measures at construction sites, promoting the use of low-emission construction equipment. |
| Other Sources | Various pollutants | 10% | Addressing smaller sources through a combination of regulations and public awareness. |
Seasonal Variations in Air Pollution
Air pollution in Los Angeles exhibits significant seasonal variations. Summer months often see higher ozone levels due to increased sunlight and heat, which accelerates photochemical reactions involving NOx and VOCs from vehicle exhaust and industrial emissions. Winter months, however, tend to experience higher levels of particulate matter, often exacerbated by wildfires and inversions that trap pollutants near the ground.
These seasonal shifts necessitate targeted mitigation strategies that adapt to changing conditions.
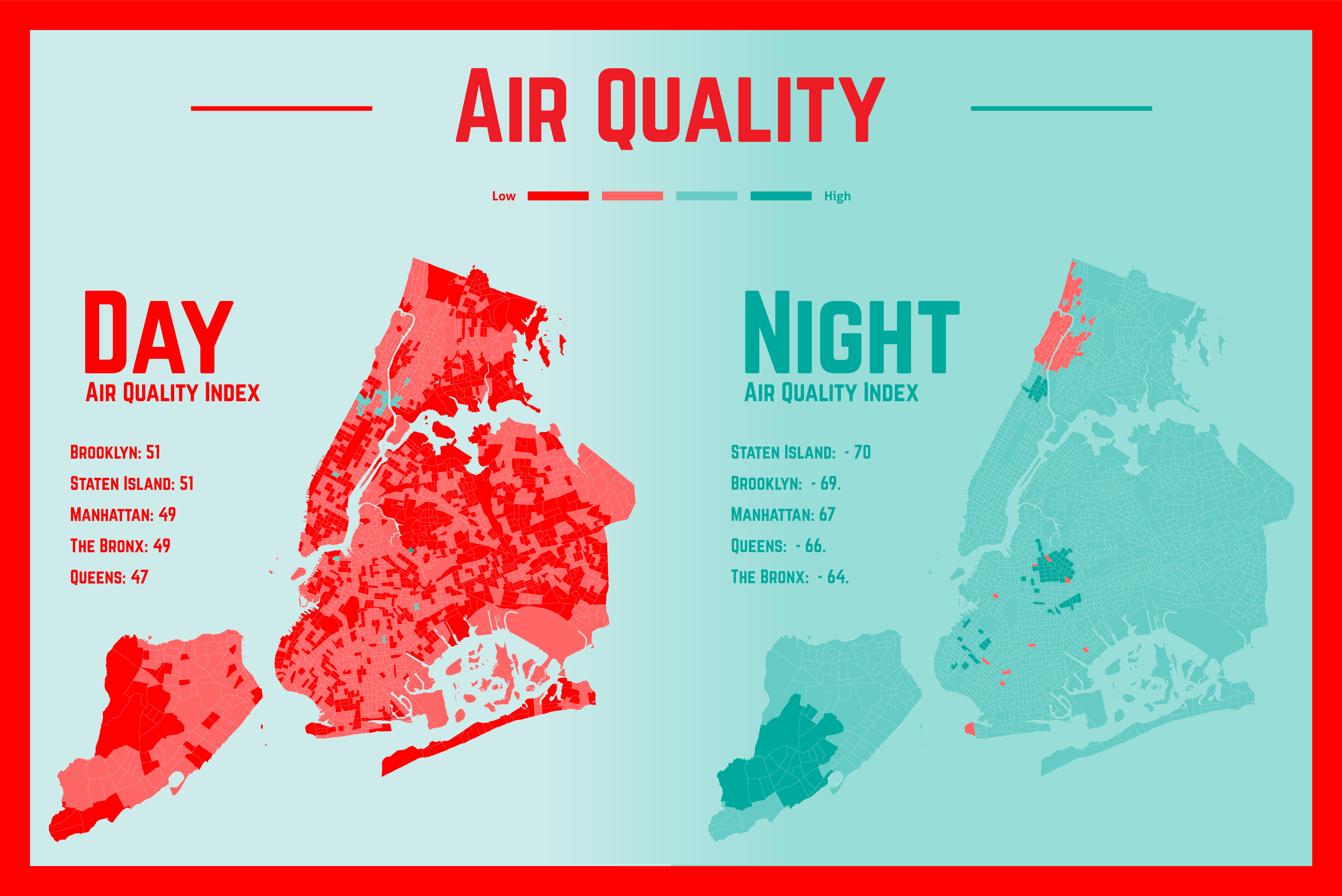
Air Pollution Profiles Across Los Angeles Neighborhoods
Air quality varies considerably across different neighborhoods in Los Angeles. Communities located near major freeways or industrial areas typically experience higher levels of pollution compared to those in more residential or suburban areas. Socioeconomic factors also play a significant role, with lower-income communities often bearing a disproportionate burden of air pollution exposure due to proximity to pollution sources and limited access to resources.
Impact of Air Pollution on Public Health
The health consequences of Los Angeles’ poor air quality are significant and far-reaching, impacting a wide range of populations. Respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular diseases, and other health problems are directly linked to prolonged exposure to air pollutants.
Health Consequences of Air Pollution
- Respiratory Illnesses: Asthma, bronchitis, pneumonia, and other respiratory issues are exacerbated by air pollution, leading to increased hospitalizations and emergency room visits.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Air pollution contributes to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems by damaging blood vessels and increasing inflammation.
- Other Health Problems: Studies have linked air pollution to increased risks of cancer, reduced lung function, developmental problems in children, and premature death.
Disproportionate Impact on Vulnerable Populations
Children, the elderly, and low-income communities are disproportionately affected by air pollution due to their increased susceptibility to its harmful effects and often limited access to healthcare resources. Children’s developing respiratory systems are particularly vulnerable, while the elderly may have pre-existing conditions that are worsened by air pollution exposure. Low-income communities frequently reside closer to pollution sources, intensifying their risk.
Specific Health Risks Associated with Common Air Pollutants
- Ozone (O3): Respiratory irritation, coughing, chest pain, reduced lung function.
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): Respiratory and cardiovascular problems, aggravated asthma, premature death.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): Respiratory infections, asthma, increased susceptibility to respiratory illnesses.
Air Quality Monitoring and Data
Monitoring air quality in Los Angeles involves a sophisticated network of sensors and monitoring stations that collect data on various pollutants. This data is then used to calculate the Air Quality Index (AQI) and to inform public health advisories and policy decisions.
Air Quality Monitoring Methods
Source: huffpost.com
In this topic, you find that Cat Bird Flu is very useful.
The South Coast Air Quality Management District (SCAQMD) employs a network of monitoring stations strategically placed throughout the Los Angeles basin. These stations use sophisticated instruments to measure concentrations of various pollutants, including ozone, particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide. Data is collected continuously and made publicly available. Mobile monitoring units also supplement the fixed stations, providing data from a wider range of locations.
Current Air Quality Index (AQI) Levels
Note: The following data is hypothetical and for illustrative purposes only. Actual AQI data should be obtained from the SCAQMD website.
| Area | AQI | Air Quality Category |
|---|---|---|
| Downtown LA | 105 | Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups |
| Pasadena | 78 | Moderate |
| Santa Monica | 62 | Good |
Hypothetical Air Quality Data Infographic
A hypothetical infographic illustrating air quality data collection and interpretation might include a map of Los Angeles showing the locations of monitoring stations, color-coded to represent AQI levels. Data visualizations, such as bar graphs showing pollutant concentrations over time, and pie charts showing the contribution of different pollution sources, would provide a clear picture of the air quality situation.
The infographic could also include icons representing health risks associated with different AQI levels, promoting public awareness and encouraging responsible behavior.
Regulations and Policies to Improve Air Quality
Los Angeles has implemented numerous regulations and policies to address its air quality challenges. These measures aim to reduce emissions from various sources and improve overall air quality. However, ongoing efforts are needed to further enhance these regulations and address remaining challenges.
Existing Regulations and Policies
The SCAQMD plays a central role in regulating air pollution in the region. Key regulations include emission standards for vehicles, industrial facilities, and other sources. Incentive programs for cleaner technologies and public awareness campaigns also contribute to improving air quality. The region also participates in broader state and federal programs to address air pollution on a larger scale.
Areas for Improvement in Regulations, Los Angeles Air Quality
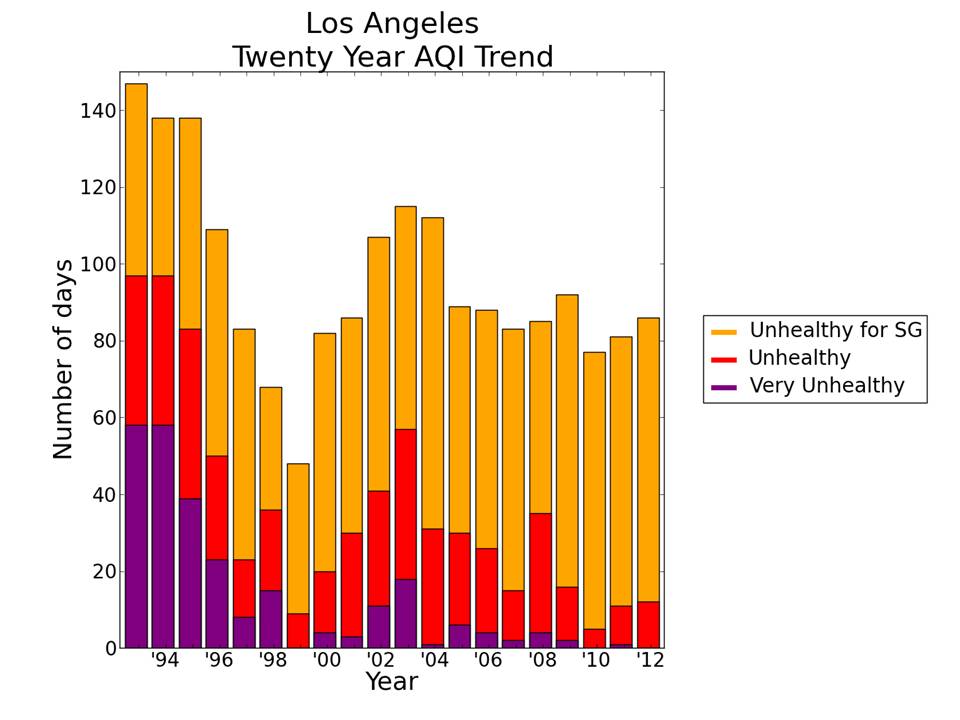
Source: blogspot.com
While existing regulations have made progress, areas for improvement include strengthening emission standards for older vehicles and industrial facilities, further incentivizing the adoption of cleaner technologies, and expanding public transportation options. Addressing the impact of wildfires through improved forest management and controlled burns is also crucial.
Comparison with Other Metropolitan Areas
Compared to other major metropolitan areas, Los Angeles’ air quality regulations are relatively stringent, reflecting the severity of its historical air pollution problems. However, continuous improvement and adaptation are needed to keep pace with technological advancements and evolving challenges. Comparing best practices and regulatory frameworks from other cities can inform future strategies.
Technological Solutions and Innovations
Technological advancements play a vital role in reducing air pollution in Los Angeles. A range of innovative solutions are being implemented and further developed to improve air quality. These include electric vehicles, renewable energy sources, and advanced filtration systems.
Examples of Technological Innovations
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): EVs significantly reduce tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air. However, the electricity used to charge EVs must also come from clean sources to maximize their environmental benefits.
- Renewable Energy Sources (Solar, Wind): Transitioning to renewable energy sources for electricity generation reduces emissions from power plants, a significant source of air pollution.
- Advanced Filtration Systems: These systems can remove pollutants from industrial emissions and other sources, significantly reducing their impact on air quality.
Potential of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies such as carbon capture and storage, advanced battery technologies for EVs, and improved air purification systems hold significant potential for further improving air quality. Research and development in these areas are crucial for achieving more substantial reductions in pollution.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Technologies
- Electric Vehicles:
- Advantages: Zero tailpipe emissions, reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
- Disadvantages: High initial cost, limited range in some models, electricity generation needs to be clean.
- Renewable Energy Sources:
- Advantages: Reduced greenhouse gas emissions, sustainable energy source.
- Disadvantages: Intermittency (solar and wind), land use requirements, initial investment costs.
- Advanced Filtration Systems:
- Advantages: Highly effective in removing pollutants, adaptable to various applications.
- Disadvantages: High initial and maintenance costs, disposal of filters requires careful consideration.
Community Engagement and Public Awareness
Community engagement and public awareness are critical to effectively addressing air pollution in Los Angeles. Active participation from residents and businesses is essential for implementing and enforcing effective air quality improvement strategies.
Role of Community Engagement
Community engagement involves actively involving residents, businesses, and other stakeholders in developing and implementing air quality solutions. This includes providing opportunities for input on policy decisions, supporting community-based initiatives, and promoting responsible behavior. Collaborative efforts are essential for achieving meaningful and sustainable improvements.
Examples of Successful Community-Based Initiatives
Numerous community-based initiatives have demonstrated success in addressing air pollution. Examples include community gardens that improve air quality and provide access to fresh produce in underserved areas, and neighborhood clean-up events that remove litter and reduce sources of dust and pollution. Educational programs in schools can also instill responsible environmental behavior in younger generations.
Strategies for Increasing Public Awareness
Increasing public awareness about air quality issues requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes public service announcements, educational campaigns in schools and community centers, and the use of social media and other digital platforms to disseminate information. Making air quality data readily accessible to the public is also crucial for promoting informed decision-making and encouraging responsible behavior.
Last Point: Los Angeles Air Quality
Ultimately, the quest for better Los Angeles air quality is a multifaceted challenge demanding collaboration between government, industry, and the community. While progress has been made, significant hurdles remain. From transitioning to cleaner transportation and energy sources to implementing stricter regulations and fostering greater public awareness, a collective effort is essential to ensure a healthier future for all Angelenos.
The fight for cleaner air isn’t just about numbers on an AQI report; it’s about the quality of life, the health of our families, and the legacy we leave behind.